Warming and Higher Rainfall Could Be a Recipe for Phytoplankton Success

Historical records from seabed sediment cores have revealed that the warming climate and increased rainfall in Australia’s North West could in fact be creating ideal conditions for the increased production of phytoplankton, one of nature’s most important indicators of ocean health.
The findings from the study: Phytoplankton Responses to Climate‐Induced Warming and Interdecadal Oscillation in North‐Western Australia, published in the journal Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, are the first to confirm these patterns.
The sediment cores were collected as part of the Western Australian Marine Science Institution’s Kimberley Marine Research Program from three bays along the Kimberley coastline, including Roebuck Bay off Broome, Koolama Bay off King George River, and Cygnet Bay in King Sound.
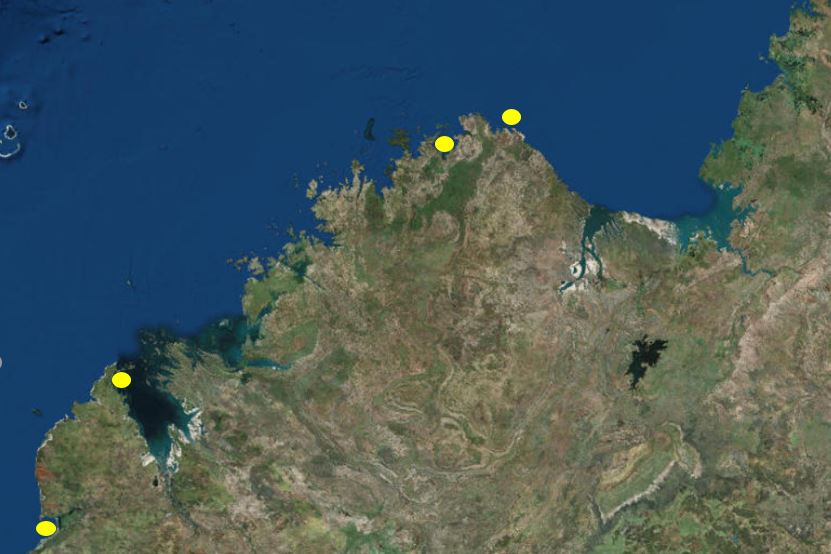 |
| Above: Sediment cores were collected from 3 bays – Roebuck Bay off Broome, Koolama Bay off King George River, and Cygnet Bay in King Sound.
|
Lead researcher Dr John Keesing from CSIRO’s Ocean and Atmosphere said the results were surprising given that warming of the ocean had been forecast to reduce phytoplankton productivity in tropical/subtropical oceans, through increasing stratification of the water column, locking deep-water nutrients away from productive surface layers, and through temperatures exceeding the thermal tolerance of some phytoplankton species.
“What we found is that up to three times more phytoplankton biomass has been produced since the 1950s along a large section of the Kimberley coast,” Dr Keesing said. “The majority of that can be linked with climate change induced increases in sea surface temperature, strong tidal mixing of coastal waters and increased rainfall creating improved nutrient supply conditions, feeding phytoplankton growth and production in shallow coastal waters.”
 |
 |
|
 |
||
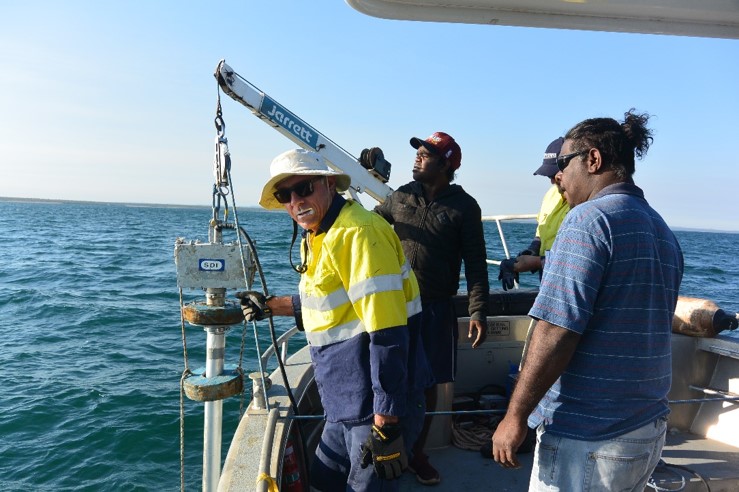
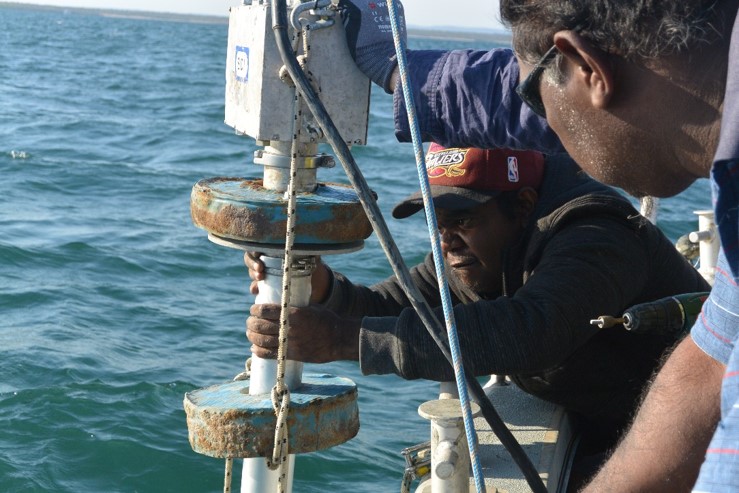
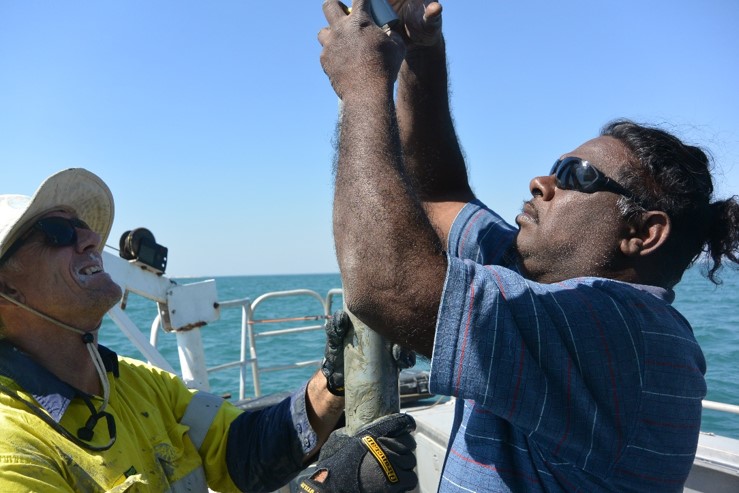
| Above: John Keesing obtaining cores in the Kimberley with the assistance from Traditional Owners from Kalumburu and Wyndham
|
||
The study also found that 20.4 per cent of the variation in phytoplankton biomass was related to long-term changes in the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation (IPO) which has an important influence on coastal nutrient supply. The positive, or warm phase of the IPO, is associated with a weaker Indonesian Through Flow (ITF) current , which enhances upwelling, a process which brings nutrients from deep water to shallow coastal waters. The present, negative or cool phase of the IPO has the opposite effect, with a strong ITF suppressing upwelling and restricting nutrient supply from the deep ocean.
“We predict that the negative impact of rising temperatures on phytoplankton in northwestern Australia could be buffered by increasing rainfall, perhaps associated with more tropical cyclones, evolutionary adaptation of local phytoplankton species to warm conditions and the upcoming warm phase of Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation,” Dr Keesing said.
Links
Yuan Z, Liu D, Masqué P, Zhao M, Song X, Keesing J K (2020) Phytoplankton Responses to Climate‐Induced Warming and Interdecadal Oscillation in North‐Western Australia. Paleoceaonography and Paleoclimatology doi:10.1029/2019PA003712
The $30 million Kimberley Marine Research Program is funded through major investment supported by $12 million from the Western Australian government co-invested by the WAMSI partners and supported by the Traditional Owners of the Kimberley.

