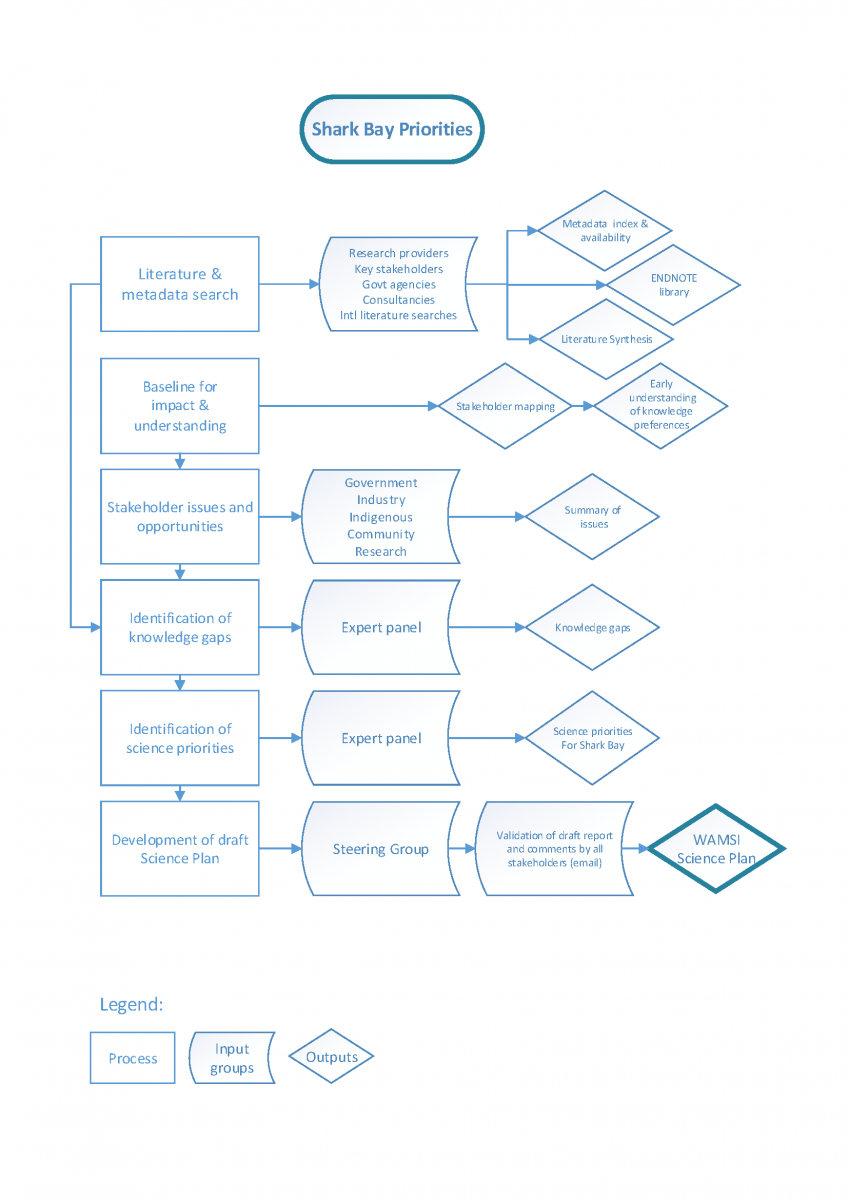
Seafood Industry Hall of Fame honour for WAMSI Research Director
Feature Image: Worthy recipients of this year’s 2019 National Seafood Awards. Left to right: Jim Mendolia, Dr. Jenny Shaw, Alex Ogg, Greg Jenkins and Justine Arnold (Photo: Courtesy WAFIC)
Western Australian Marine Science Institution (WAMSI) Research Director, Dr Jenny Shaw, has been recognised at the 2019 National Seafood Industry Awards for her long-standing commitment to fisheries in Australia.
Jenny was inducted into the National Seafood Industry Hall of Fame in Melbourne at Australia’s biggest biennial celebration of the seafood industry, along with fellow Western Australians Greg Jenkins and Jim Mendolia, and Dawn Jordan from Tasmania.
The WA Fishing Industry Council (WAFIC) Chief Executive Officer Alex Ogg said that the awards were a well-deserved acknowledgement to showcase and reflect on the achievements throughout Australia’s seafood industry, and an incredible success for WA’s contributions at a national scale.
“Jenny, Greg and Jim have all been pivotal in the development of WA’s seafood industry. Jenny has a long history with the seafood industry having occupied roles in fisheries and marine related areas for her entire working career,” Mr Ogg said.
“As an industry body, we recognise the importance of acknowledging those individuals and organisations who make a substantial contribution to benefiting and promoting our industry, and these winners are certainly worthy of this recognition. We are incredibly proud of their achievements,” Mr Ogg concluded.
WAMSI CEO Dr Luke Twomey congratulated Jenny saying her knowledge of fisheries, the respect she has in the industry and her strong leadership skills were a tremendous asset to the Institution.
“Jenny has been actively involved in a lifetime of change in fisheries and marine areas within the government and private sectors in Australia and internationally,” Dr Twomey said. “She is a great asset to marine science in Western Australia and WAMSI as we forge ahead with identifying regional science priorities and developing protocals and processes for Indigenous engagement with scientists on Country.”
Jenny was a founding member and inaugural Director of the Women’s Industry Network Seafood Community. She has been a mentor for a number of highly successful women in the industry and has always been available both formally and informally for strategic advice, technical knowledge and confidence building. She is one of only four life members of the organisation and last year was inducted onto their Honour Role and has been instrumental in helping the development of a similar organisation in Ireland.
As an accomplished speaker at State, National and International Conferences and workshops, Jenny has been able to increase the visibility of the seafood industry on a large stage. Recently she was a speaker and panel member at the World Seafood Congress in Reykjavik, Iceland addressing the invisibility of women in the seafood industry and the consequences from often-unintended policy impacts.
Dr Shaw said it was an honour to be inducted into the National Seafood Industry Hall of Fame.
“It’s a great honour to receive this recognition and I’m particularly proud of the fact that this year the industry inducted two women, myself and Dawn Jordan, to the Hall of Fame,” Jenny said. “As Research Director at WAMSI I remain a strong advocate for commercial fishers and the value of a well-managed, well-researched commercial fishing industry with strong and diverse fisher voices as part of decision making.”
Click here to view the full WAFIC media release and list of winners

 A large number of lead scientists (35), both local and international have been formally approached to contribute to the project by providing publications and metadata of their Shark Bay research.
A large number of lead scientists (35), both local and international have been formally approached to contribute to the project by providing publications and metadata of their Shark Bay research.